Cameras Module
Video capture from CSI cameras (Raspberry Pi) and USB webcams with per-frame timing data.
Each camera runs in its own module instance. Multiple cameras can record simultaneously. USB cameras support optional audio recording.
Getting Started
- Connect your camera — CSI ribbon cable or USB
- Enable "Cameras" — In the Modules menu
- Camera appears — In the Devices panel when detected
- Click Connect — To launch this camera's window
- Adjust settings — Via the View menu if needed
- Start a session — To begin recording
User Interface
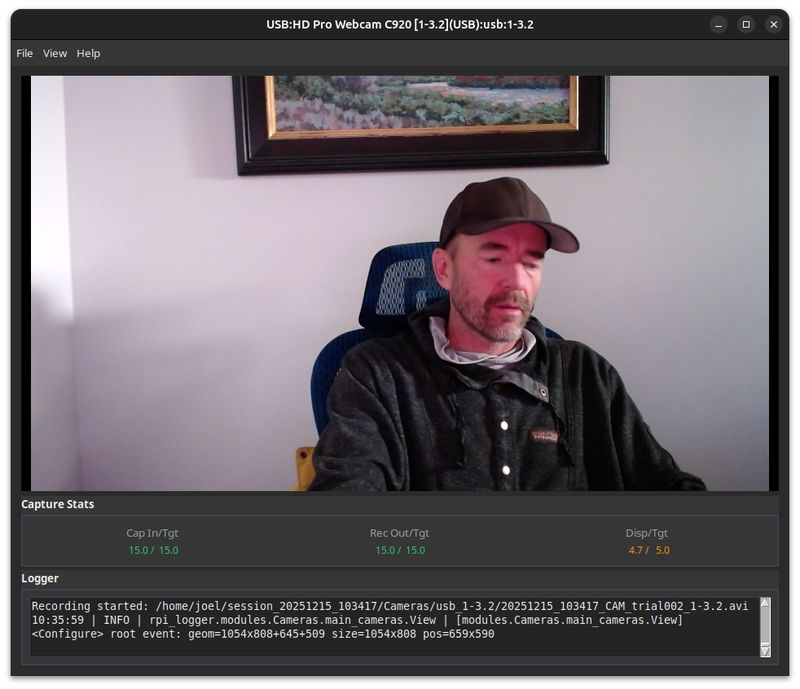
The preview runs at reduced resolution for performance—this does not affect recording quality.
Metrics Panel
| USB Cameras | CSI Cameras | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Cap In/Max | Actual frame rate from camera |
| Record | Rec Out/Tgt | Frame rate being written to disk |
| Preview | Disp/Tgt | Display frame rate |
| Audio | — | Audio recording status |
Metrics are color-coded: green (healthy), orange (stressed), red (problem). See Performance for details.
Data Output
File Location
| Camera Type | Output Directory | Example |
|---|---|---|
| USB Camera | {session_dir}/Cameras/{device_id}/ |
~/recordings/session_001/Cameras/usb_1-2.3/ |
| CSI Camera | {session_dir}/picam{N}/ |
~/recordings/session_001/picam0/ |
Files Generated
| File | Description |
|---|---|
trial_001.mp4 |
Video file (USB cameras - H.264, with optional AAC audio) |
trial_001.avi |
Video file (CSI cameras only - MJPEG) |
trial_001_timing.csv |
Per-frame timing data |
Video File Format
| Camera Type | Container | Video Codec | Audio Codec |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB cameras (audio enabled) | MP4 | H.264 | AAC |
| USB cameras (audio disabled) | MP4 | H.264 | — |
| CSI cameras (Pi only) | AVI | MJPEG | — |
Timing CSV Columns
The timing CSV contains per-frame timing for precise synchronization with other modules (9 columns).
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
trial |
Trial number (integer) |
module |
Module name ("USBCameras" or "CSICameras") |
device_id |
Camera device identifier |
label |
Optional trial label (may be empty) |
record_time_unix |
Wall clock time when captured (Unix seconds, 6 decimals) |
record_time_mono |
Monotonic time when captured (seconds, 9 decimals) |
frame_index |
1-based frame number in video file |
sensor_timestamp_ns |
Hardware sensor timestamp in nanoseconds (CSI cameras only, 0 for USB) |
video_pts |
Presentation timestamp in video stream |
Synchronization
All RSLogger modules share the same clock. Use record_time_mono to correlate video frames with events from other modules (DRT, VOG, Eye Tracker, Audio, GPS).
To find the video frame at a specific time:
- Find the event's
record_time_monoin the other module's data - Find the closest
record_time_monoin the camera timing CSV - Use that row's
frame_indexto seek in the video file
Camera Types
| Feature | CSI Cameras | USB Cameras |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Raspberry Pi only | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| Hardware timestamps | Yes (sensor_timestamp_ns) |
No (use record_time_mono) |
| Audio recording | No | Yes (optional, from built-in mic) |
| Video format | AVI (MJPEG) | MP4 (H.264) |
| Hot-pluggable | No | Yes |
Supported CSI Sensors
IMX296 (global shutter), IMX708 (12MP autofocus), IMX219, IMX477, and other libcamera-supported sensors.
USB Camera Notes
- Any UVC-compliant webcam
- Actual FPS may vary from requested depending on lighting and USB bandwidth
Configuration
Access via View > Camera Settings...
| Setting | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 640x480 | Higher resolution = larger files, more CPU |
| Frame Rate | 30 | Options: 1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60 |
| Preview Scale | 1/4 | Does not affect recording quality |
| Audio Mode (USB only) | auto | auto, on, or off |
Performance
Metrics Color Coding
- Green — Healthy (95%+ of target)
- Orange — Stressed (80-95%)
- Red — Problem (below 80%)
Multiple USB Cameras
Cameras on the same USB bus share bandwidth. If FPS drops when adding cameras, connect them to different USB controllers (front vs back ports, or a PCIe USB card).
Storage
Use a fast SD card (Class 10 / U3) or SSD. Typical file sizes at 30fps 720p:
- USB cameras (MP4/H.264): 2-4 GB/hour
- CSI cameras (AVI/MJPEG): 3-8 GB/hour
Troubleshooting
Camera not detected
- Check physical connection
- Check if another application is using the camera
- On Raspberry Pi:
libcamera-hello --list-cameras - On Linux:
v4l2-ctl --list-devices - On macOS/Windows: Check camera permissions
Low frame rate or dropped frames
- Lower frame rate (biggest impact)
- Lower resolution
- Improve lighting (cameras slow in low light)
- Use faster storage
- Try a different USB port
Preview is laggy
Lower preview scale to 1/4 or 1/8. Preview settings don't affect recording quality.
Audio out of sync
Verify the frame rate setting matches the actual Hardware FPS shown in the metrics panel.
